While Loop Examples
int X =
1;
while (X <= 5)
{
System.out.print("Yes");
X++;
}
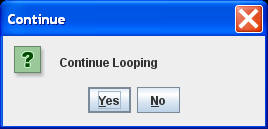
int Continue = 0;
while (Continue <= 0)
{
"Continue Looping","Continue",0,3);
}
Java Notes 5 – Control Statements
If, While, For
5.1 If Statement
The if statement allows your program to make a decision. The following
operators may be used:
< > <= >=
== != || && !
|
If Statement Examples |
|
|
int A =
5; |
A is greater than 3 |
|
double Salary = 12.75; if (Salary > 15.0) System.out.println("You are well paid"); else System.out.println("You should work harder"); |
You should work harder |
|
// an if statement float HoursWorked = 45.0; float Wage = 10.0 if (HoursWorked > 40.0) { System.out.println("You worked overtime"); Wage = Wage * 1.5; } |
You worked overtime |
|
|
You make too little or too much |
|
|
You have a good wage |
|
int Age = 25; if (Age < 10) System.out.println("You are less than 10"); else if (Age < 20) else if (Age < 30) else System.out.println("You are over 30"); |
|
5.2 While Loop
The while loop will execute a body of statements continuously as long as the condition is true.
|
While Loop Examples |
|
|
int X =
1; |
YesYesYesYesYes |
|
int Continue = 0; while (Continue <= 0) { "Continue Looping","Continue",0,3); } |

|
5.3 For Loop
A for loop is useful when a set number of iterations is known. After
the for statement, there are three sections in the parenthesis:
1. Initialize the control variable - executes once at the beginning of the loop
2. Condition - test if true before each iteration
3. Increment the control variable after each iteration
|
For Loop Examples |
|
|
for (int
i = 1; i <= 10; i++) |
12345678910 |
|
for (int j = 8; j < 1; j--) System.out.print(i); |
8765432 |
|
// statements in the loop for (int count = 1; count <= 20; count++) { System.out.print(count + "\t"); if (count % 4 == 0) System.out.println(); } |
1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
for (int x = 1; x <= 8; x++) { for (int j = 1; j <= x; j++) System.out.print("*"); System.out.println(); } |
* ** *** **** ***** ****** ******* ******** |
1. Create a program named sentence.java. Ask the user to enter a
sentence. Output the number of vowels, consonants, and words in the
sentence.
Hint: Create int variables V, C, and W. Create a for loop
that steps through each character in the sentence and increments the appropriate
variable.
2. Create a program named forloop.cpp. Declare the following arrays:
double[] HourlyWage =
{7.25, 10.75, 12.0, 8.55, 9.5, 20.0, 15.0, 11.75};
String[] Employees = {"Sam", "Ben", "Joie", "Holly", "Marcus", "Mini", "Max", "Tosh"};
Write a for loop that steps through each element of the arrays. Output each employees, name and hourly wage. Output the sum of all hourly wages. Output the average hourly wage.
3. Create a program named roman.java. Ask the user to enter a Roman
Numeral. Output the numeric value of the Roman
Numeral.
Test your program with these numbers: MCMXLII,
MCMLXIX, DCCCLXXXVIII
| Hint: | Create a for loop that steps through each character of roman
numeral. M = 1000, D = 500, C = 100, L = 50, X = 10, V = 5, I = 1. MDCLXVI = 1000 + 500 + 100 + 50 + 10 + 5 + 1 = 1666 If a digit is out of order, then it is subtracted from the next digit. This is only used for these combinations: CM = 900, CD = 400, XC = 90, XL = 40, IX = 9, IV = 4 |